In order to improve production efficiency and save manpower, general production lines adopt automated operations, and ordinary hydraulic presses cannot meet production needs. So, what aspects are involved in the advanced technology of high-speed hydraulic press production lines?
■ Balance Device
The hydraulic balance cylinder utilizes the self-weight of the slider and the hydraulic oil pressure in the hydraulic cylinder to achieve balance and offset the self-weight of the slider; the hydraulic balance cylinder is controlled through the hydraulic valve by the hydraulic cylinder and the large-capacity accumulator station. When the balance cylinder is used for balancing, only a small power source is needed to achieve the rise and fall of the slider. The use of the balance cylinder can effectively reduce the power consumption when the slider is pressed, and also reduce the power consumption when the slider quickly returns; the effective application of the balance cylinder can greatly reduce power consumption, thereby reducing production costs. The following figure shows a balancing device in a certain high-speed production line.
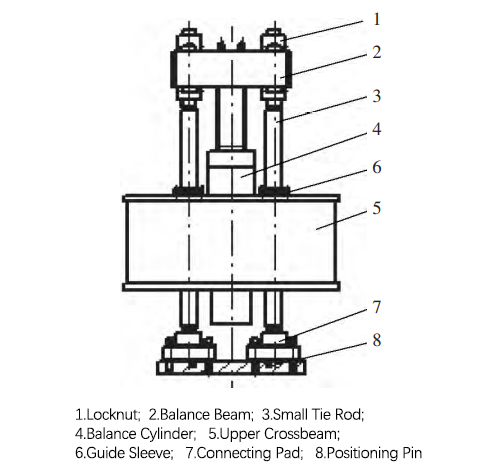
■ Anti-Deviated Load Guide Device
The fast descent speed and return speed of high-speed hydraulic presses are much higher than those of ordinary hydraulic presses, and the frequency of workpiece pressing is also high, with some workpieces still exhibiting deviated load. High-speed hydraulic presses have high requirements for the strength of the machine frame, generally requiring a ratio of 1/6000 or even better. To resist the deviated load during stamping, a four-cornered bidirectional adjustable inclined wedge guide device can be used. High-strength bolts are used to connect the 45 steel forging guide rail body to the processing surface of the pillar side. Two composite material guide plates are installed on both sides of the guide rail body to increase the guide rail pressure ratio and enhance the equipment's resistance to deviated load. By adjusting the inclined surface of the wedge-shaped adjusting block to adjust the gap between the slider guide plate and the guide rail body to meet the equipment's requirements for accuracy. As shown in the following figure.
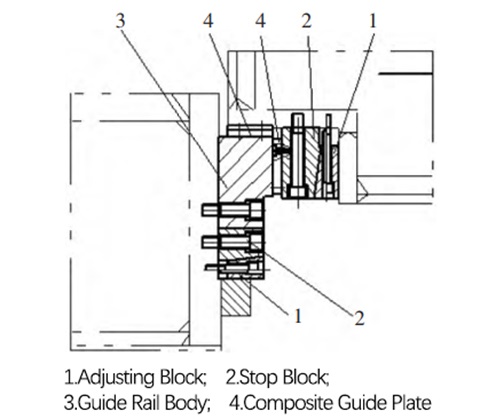
■Fast Oil Cylinder Structure
One of the important issues to be addressed in the design process of high-speed hydraulic cylinders is the stability of the cylinder operation. The piston rod of the cylinder has a certain mass, and when driven by hydraulic pressure to move downward, it will generate a significant impact force, leading to mechanical collisions and noise. With the increase in equipment operating speed, how to smoothly transition from fast to slow speed becomes a primary concern. In order to achieve a smooth transition between fast and slow speeds of the hydraulic cylinder, a buffering effect can be achieved by reducing the amount of oil discharged from the lower chamber when the main cylinder piston rod quickly inserts into the cylinder port bushing during the downward movement; a special design can be implemented at the upper end of the return cylinder piston rod and the end of the hydraulic cylinder return to increase the speed of oil discharge during the return, thereby increasing the oil discharge resistance to achieve a buffering effect.
■Hydraulic Cushion Structure
The hydraulic cushion is located inside the lower beam, and depending on the size of the table, a three-cylinder or five-cylinder structure can be used for the hydraulic cushion cylinder, with the middle cylinder being a piston cylinder and the remaining cylinders being plunger cylinders. The quick ejection action is completed by the ejection cylinder, and when the slider moves downward and the mold contacts the workpiece, the hydraulic cushion passively retracts through the ejection rod and pressure ring to complete the edge pressing action during the mold closing process, controlling the reasonable flow of the workpiece material.
The hydraulic control system of the hydraulic cushion adopts hierarchical ejection, facilitating the control of ejection speed. The hydraulic control system of the hydraulic cushion also uses hierarchical tension control, enabling precise control of the hydraulic cushion force for small tonnage hydraulic presses. The slider and hydraulic cushion pressure and position of a hydraulic machine can be digitally controlled. The stretching process is divided into: fast downward movement of the slider, simultaneous slow downward movement of the slider with passive retraction of the hydraulic cushion, holding pressure, pressure relief, slow return, fast return, and deceleration to stop. When there is an independently driven hydraulic cushion pump group, the hydraulic cushion reaches the ejection position just as the slider returns. During the passive retraction of the hydraulic cushion, the oil pressure for oil discharge is traditionally controlled using a proportional valve and a displacement sensor, setting one or more current values based on the displacement to achieve different pressure levels. If the workpiece requires different pressure levels at the corners, four proportional valves can be used to individually control the pressure at each corner. The precision of pressure control depends on various factors such as the speed of the slider, the response speed of the proportional relief valve element, the temperature of the oil, the machining accuracy of the cylinder, the length of the pipeline, the volume of oil in the cylinder, the cleanliness and viscosity of the oil.
XIRO-electric servo press/XIRO-hydraulic press/XIRO-mechanical powder compacting press
XIRO, an automated machine manufacturer, 24-hour response factory, with a professional engineering team 24 hours online technical service. All machines are CE certified, come with a 2-year warranty, and lifetime service. With 20+ years rich production experience, our equipment is exported to more than 60 countries. We provide customizable press machines and comprehensive productivity solutions, ensuring it's the most competitive, accurate solution to any assembly requirement! XIRO wishing you prosperity!
 |  |  |






