A hydraulic pump is an energy conversion device that converts the mechanical energy of a drive motor into the pressure energy of oil to meet the needs of driving external loads in the actuator, and is the main component of a hydraulic power mechanism.
Working principle of hydraulic pump
Currently, the working principle of hydraulic pumps used in hydraulic systems is almost the same, which relies on the change in the volume of the working chamber with hydraulic seals to achieve oil suction and pressure, hence they are called volumetric hydraulic pumps.
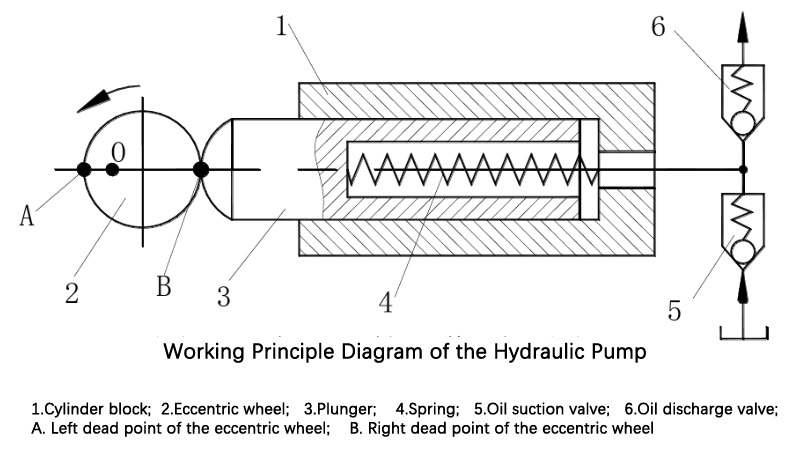
The working principle of a volumetric hydraulic pump is very simple. Taking a single plunger hydraulic pump as an example, it is similar to a medical syringe, and when paired with an automatic flow control device, it is ready for use.
In general, for a hydraulic pump to work properly, it must meet four conditions:
1) It must have a sealed volume (sealed working chamber);
2) The sealed volume must be able to change alternately;
3) It must have a flow control device (isolating the suction chamber and discharge chamber);
4) The oil tank must be in communication with the atmosphere during the oil suction process.
Classification
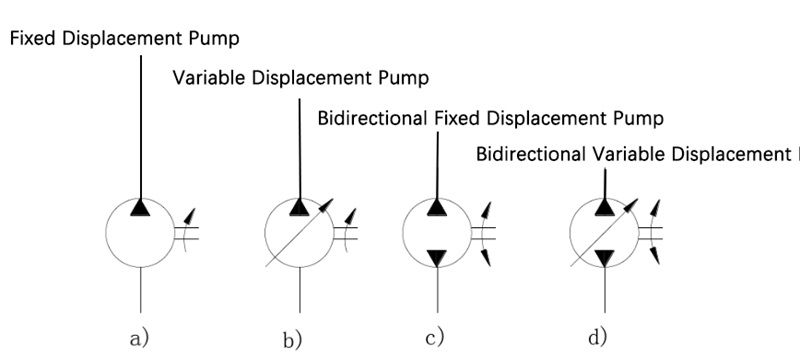
According to whether the volume of oil output by the pump unit changes within a certain period of time, pumps can be classified into quantitative pumps and variable pumps.
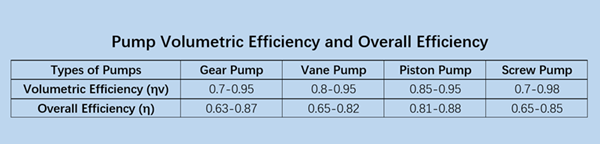
According to the structural form, they can be divided into gear pumps, vane pumps, plunger pumps, and screw pumps, as shown in the figure below.
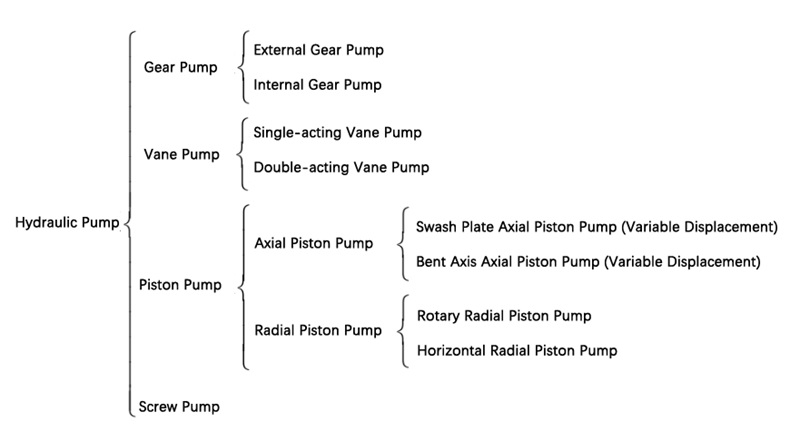
Their respective advantages, disadvantages, and working pressures are as follows:
- Gear pump
Advantages: simple structure, reliable work, easy maintenance, low price, strong self-priming ability;
Disadvantages: prone to vibration and noise, large leakage, low volumetric efficiency, radial hydraulic pressure imbalance, non-adjustable flow rate;
Working pressure: generally used for low pressure.
- Vane pump
Advantages: uniform oil delivery, low pressure pulsation, high volumetric efficiency;
Disadvantages: complex structure, difficult to add vanes prone to being blocked by dirt
Working pressure: medium pressure
- Plunger pump
Advantages: compact structure, small radial size, high volumetric efficiency;
Disadvantages: complex structure, relatively expensive;
Working pressure: high pressure
- Screw pump
Advantages: simple structure, small volume, light weight, smooth operation, low noise, long service life, strong self-priming ability, high volumetric efficiency.
Disadvantages: complex screw tooth shape, difficult to process, difficult to guarantee accuracy;
Working pressure: 4~40MPa
Hydraulic pump performance parameters
1. Pressure
(1) Rated pressure P0
Under normal working conditions, the highest pressure at which the hydraulic pump is allowed to operate continuously according to the test standards. Generally, the rated pressure is the nominal pressure of the pump.
(2) Maximum allowable pressure Pmax
According to the test standards, the highest pressure that can be briefly operated beyond the rated pressure.
(3) Working pressure P
The specific pressure value reached by the pump during actual operation.
2. Displacement and Flow Rate
Displacement q refers to the volume of liquid discharged by the main shaft of a hydraulic pump for each rotation, calculated based on its geometric dimensions. This is known as the pump's displacement or geometric displacement, and the commonly used unit is mL/r.
A hydraulic pump with adjustable displacement is called a variable pump, while one with a constant displacement is called a fixed-displacement pump.
(1) Theoretical flow rate Qt, refers to the volume of liquid discharged per unit time under ideal conditions without considering leakage from the hydraulic pump, and the unit commonly used is L/min.
If the pump's displacement is Q and the main shaft speed is n, then the pump's theoretical flow rate Q is:
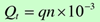
(2)Leakage flow ΔQ, refers to the liquid leakage through the clearances of the moving parts in the pump, also known as volumetric loss of the pump.
Leakage flow is divided into internal leakage and external leakage.
➢ Internal leakage refers to the leakage from the discharge chamber of the pump to the suction chamber, which is difficult to measure directly.
➢ External leakage refers to the leakage from the suction and discharge chambers of the pump to other free spaces, which can be easily measured.
The amount of leakage flow depends on factors such as the sealing of the pump, working pressure, and liquid viscosity.
(3)Actual flow rate Q refers to the volume of liquid actually output by the hydraulic pump in unit time when considering leakage losses.
➢ The actual flow rate is less than the theoretical flow rate, i.e. Q = Q - ΔQ.
(4) Rated flow rate Q0, refers to the flow rate that must be ensured under normal working conditions, as specified by the test standard (rated pressure and rated speed), shown on the product sample or nameplate.
3. Power and Efficiency
Theoretical output power pt:
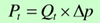
Actual output power P:
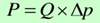
Volumetric efficiency ηv:
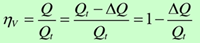
In practice, the actual flow rate is often calculated according to the following formula:
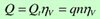
Input power pi and overall efficiency η
Input power pi:
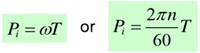
Mechanical efficiency ηm
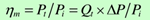
Overall efficiency η:
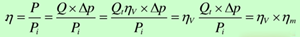
Volumetric efficiency decreases as pressure increases; mechanical efficiency initially increases rapidly, then slows down; overall efficiency starts at zero and has a maximum value.
4. Speed
The rated speed n0, refers to the maximum speed at which the pump can continuously operate under rated pressure for a long period of time, commonly measured in r/min;
The maximum speed nmax, refers to the maximum speed at which the pump can operate for a short period of time under rated pressure;
The minimum speed nmin is the minimum speed at which the pump can operate normally.
The common rated speed ranges for various types of hydraulic pumps are as follows:
- Gear pumps: 1000-1800 r/min;
- Vane pumps: 1000-1800 r/min;
- Axial piston pumps: 1000-2200 r/min.
How to choose a hydraulic pump for daily work?
Based on the working conditions of the main unit, power size, and the system's requirements for performance, first determine the type of hydraulic pump, and then determine its specifications and model according to the pressure and flow rate required by the system. In the field of hydraulic machines, double-acting vane pumps and radial piston pumps are used more frequently.
XIRO-electric servo press/XIRO-hydraulic press/XIRO-mechanical powder compacting press
XIRO, an automated machine manufacturer, 24-hour response factory, with a professional engineering team 24 hours online technical service. All machines are CE certified, come with a 2-year warranty, and lifetime service. With 20+ years rich production experience, our equipment is exported to more than 60 countries. We provide customizable press machines and comprehensive productivity solutions, ensuring it's the most competitive, accurate solution to any assembly requirement! XIRO wishing you prosperity!
 |  |  |






